Beginner’s Guide to HTPC Codecs, File Formats, Containers, Filetypes
Codecs? File types? Oh my! If you have ever tried to watch a video you downloaded from the internet only to find it unable to be played (or maybe just audio but no video), then this is the guide for you! We’re going to try to do our best to cover most of the more common file types that are out there, and what they mean to you and your home theater experience.
Before we get into the details, let’s cover the basics of the terminology. Codec is an acronym for compressing\decompressing. This technology is used to execute an algorithm to compress or decompress video or audio. An example of this is playback of your PVR recordings on your HTPC; when the file plays back your PC is decompressing, or decoding, the MPEG-2 or H.264 video and MPEG-Audio or AC-3 audio contained in the file.
- Decoding usually refers to “playback” of a certain file.
- Encoding refers to taking a raw or uncompressed signal and converting to a compressed format (i.e recording a TV stream to MPEG-2)
- Transcoding refers to changing compressed audio and/or video formats (i.e. converting MPEG-2 to H.264)
Let’s start out with some of the formats used to encode audio & video . I won’t go into a lot of detail but the common ones will be covered. To playback these formats a decoder or transform component is required, when using DirectShow this is called a filter.
- MP3 – MPEG-1, Layer 3 audio compression became popular in the ’90s due to sound quality in smaller file sizes.
- FLAC – Stands for “Free Lossless Audio Codec” which has gained a lot of popularity over the years as it can retain the files original quality while reducing the size significantly.
- MPEG-2 – Standard video compression used in DVDs, some Blu-ray discs, broadcast TV, older digital video cameras, etc. Older analog tuners used MPEG-2 to encode video.

- H.264 – (note x264 is merely a software H.264 encoder). H.264 is an emerging standard that is increasingly being used worldwide for video where MPEG-2 has been previously used.
- VC-1 – Microsoft developed alternative to H.264. This codec was used by HD DVDs and some Blu-rays

- WMV – Microsoft developed video codec
- WMA – Microsoft developed audio codec

- AAC – Advanced Audio Coding has been in existence since the late ’90s and can deliver better audio quality at a lower bitrate when compared to mp3. AAC was first defined in the MPEG-2 specification and further defined in the MPEG-4 specification with several levels of compression tools. Commonly used by Apple itunes store as a delivery format and increasingly used as an audio compression format in place of mp3.
Containers are used to store the various compressed formats listed above. When you come across a file it will be named something like *.mkv or *.avi or *.mpg. To playback these containers a source or splitter component is required.
- AVI –Short for Audio Video Interleave, one of the oldest containers developed to store media files on Windows

- MKV – Increasingly popular open source container maintained by the Matroska organization.
- MOV – Apple’s container
- ASF – Microsoft developed container intended to provide better support for progressive downloads and HTTP streaming
- WMV – An ASF file storing content compressed using WMV/WMA
- VOB – Container used to store compressed audio and video on DVDs
- MPG – Container for MPEG-2 files optimized for storage as a file, also known as a MPEG-PS or program stream
- TS – MPEG-2 transport streams are the defacto standard for use in broadcast worldwide. Digital tuners commonly receive this format and either store it directly or demultiplex the stream contents for use in another container (ie, wtv).
- DVR-MS – ASF based container used by Media Center to house MPEG-2 files, metadata and DRM for Media Center recordings
- WTV – Container developed by Microsoft and introduced with the TV Pack update to Vista Media Center (Fiji) to replace DVR-MS. Can theoretically contain most codecs but is currently used to store MPEG-2 or H.264 video and MPEG-Audio, AC-3 or AAC audio.
- M2TS – Very similar to the TScontainer used by Blu-ray discs to house video and audio files MP4 – Standard container for MPEG-4 audio and video, also known as M4V
- MPA – Standard container for AAC audio files, also known as M4A or AAC
So you might be wondering, how do I play all/any of the above file types with my brand new HTPC?
This is a bit more complicated. If you search for codecs, you will probably find various “codec packs” like “Sharky007’s Codec Pack.” If you have read all our Beginner’s Guides, you will remember that one of the most important pieces to having an HTPC is stability. While codec packs can address the “just make it play” problem in the short run because it’s a single installer that covers every codec on earth, the disadvantage to this is you are installing a lot of codecs you will never use many of which are conflicting or cannot be legally distrusted by the pack’s author, and can often cause stability issues in other programs.
Ideally, you will be able to identify which codecs you need to play and can install only those specifically. For example, if most of your files are Xvid, you can install just the Xvid codec and then your files will be able to play, and you didn’t need to install anything unnecessarily.
For a lot of people however, time is valuable or they just don’t care to track down each individual codec that they would need. For that, something like the popular FFDShow-Tryout package is pretty solid. It includes a pretty large selection of codecs but has been known to be stable all things considered.
I should note, if you are running Windows 7 64-bit and are trying to play files with subtitles (an AVI with a subtitle *.srt or *.sub file for example) then you will need to use Sharky007 Codec Pack. Please pay attention when installing any of these types of packs however, and make sure you are installing only what you need–worst case you can always install the pieces you left out, but that’s much easier than trying to clean up a system that’s unstable.
So you downloaded a file on the internet, and now it’s not playing. How can you tell what codecs are being used?
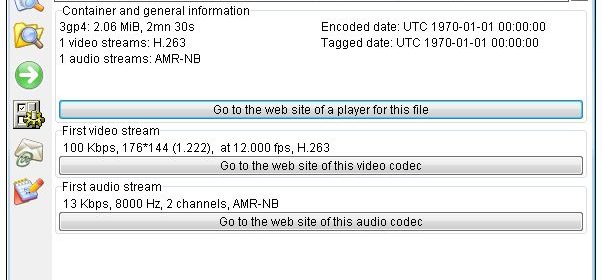
While there are a few programs available that allow you to scan a file to see what codecs are being used, our preferred program is called MediaInfo. It’s a free small utility which can even be launched directly from the context (right click) menu of the file itself, and this will show you all sorts of goodies for your video files as to what you need to get to play it.

Now you have an idea of what is going on in the file format world. Here are a few examples of this in process. For most of these examples, I am focusing on Windows 7 Media Center (7MC) and its capabilities.
Standard PVR Function
- 7MC in combination with the TV tuner encodes the TV signal to MPEG-2 or H.264 and stores it in a WTV file container.
- 7MC includes a H.264/MPEG-2 decoder with the support for PlayReady DRM. As such it has native capabilities to play back WTV files containing MPEG-2 or H.264.
DVD Playback
- A studio encodes the movie to MPEG-2 and stores it in a VOB container. Along with most commercial media, there is DRM (CSS) present on the DVD.
- Windows 7’s installed MPEG-2 decoder is compatible with the DRM necessary to playback DVDs.
Hauppauge HD PVR – H.264 Encoding
- The Hauppauge HD PVR when used with SageTV encodes the incoming analog signal to H.264 and stores the video and audio in in a ts container.
Eariler versions of Windows did not include a H.264 decoder so a 3rd party component was required, so Hauppauge includes ArcSoft’s video decoder. Windows 7 does include a H.264 decoder so it can be used to playback these files
Blu-ray![]()
- A movie studio encodes your favorite title to H.264 or VC-1 and the audio to a lossless (DTS-HD or TrueHD) and lossy format (DTS, Dolby Digital) either as a discrete track or included as part of the lossless track (referred to as “core” audio) and stores it in a .m2ts container. The file and associated Blu-ray disc structure is burned to Blu-Ray DVD. For information on playing the HD audio formats mentioned above, see our Guide to Bitstreaming HDMI HD Audio Formats from your HTPC

- While Windows 7 does include a H.264 decoder, it does not include a functional M2TS splitter or VC-1 decoder and does not support the DRM (AACS) used on Blu-ray discs so additional software is required; ArcSoft TotalMedia Theatre, Cyberlink PowerDVD and Corel WinDVD all support Blu-ray playback.

What about the PCM tracks on
What about the PCM tracks on Blu-ray? Are these not in the m2ts container as well or are they somewhere else?
Transport streams (ts or
Transport streams (ts or m2ts) do hold PCM audio.
I am really looking forward
I am really looking forward to all of this series article. It will really handy guide for HTPC beginners like me.
Thanks Mike
If you have any questions, by
If you have any questions, by all means, ask away in our forums.
Ok. Ready to tear my hair
Ok. Ready to tear my hair out. 7MC is not playing .mpg files (with H.262 if that helps). Installed KLite codec pack and still no joy. MP4 plays fine.
Sorry to say this, but you
Sorry to say this, but you should not have installed the KLite codec pack. WMC7 can play MPG files natively. If you have a recent backup from just before you installed KLite do a complete restore. Verify you can now play your MPG files and then start over to add MP4 support.
Thanks phoneguy…but my
Thanks phoneguy…but my whole reason for installing KLite in the first place was because I was getting the “Cannot open the file” error.
And, now the plot thickens. If I go to the .mpg in Windows Explorer, and “Open with Windows Media Center”, the file plays fine, but still get the error when I try to play it natively out of 7MC.
OK. Need some more
OK. Need some more information.
Is this a new install of W7? 32 or 64-bit?
Is this a HTPC, gaming PC, Desktop, etc…?
Have you installed any other playback software?
Were you ever able to play .mpg files??
W7 32-bit. not a new
W7 32-bit. not a new install.
HTPC
VLC is installed as well as Media Player Classic (came with the kLite)
I had never tried. It’s a converted PC to HTPC. Recently installed AnyDVD as well for DVD playback.
AVIs play fine, as do the mkv / mp4 type files.
Thanks in advance for the help!
Sounds .mpg files are not
Sounds .mpg files are not associated w/ WMP, or something went afoul in your registry to make .mpg files not recognized. Check your file association in control panel.
Just checked the file
Just checked the file association, and they are indeed mapped to WMP. I tried both changing it to Windows Media Center as the default program, then back to WMP, each with no joy…
Would it have something to do with WMP 12 vs 11? If I try to play them directly into WMP, it craps out as well.
Just. Plain. Frustrating.
What you are seeing usually
What you are seeing usually comes from a program changing the default Windows settings or registry. When this happens to me I usually do a clean install. If you can back-up anything important I would recommend that. Yes it is like radical surgery but sometimes it’s the best.
OMFG. So, was attempting to
OMFG. So, was attempting to solve a different challenge (speaker crackle while watching HD streamed content) when I decided to roll back my audio driver. Low and behold, the files now play natively out of 7MC. Go figure. Thanks for the advice phoneguy. Very much appreciated! Now, on to the audio…
WOW! An errant audio driver
WOW! An errant audio driver scrapped MPG playback. I’ll deff have to post-it-note that in my brain.